Expose Ports Using Tunnels
This topic explains how to expose ports on VMs and VM-based clusters created with Compatibility Matrix.
Expose Ports on VMs
You can expose ports on a VM and make them accessible on the public internet.
Limitation
Creating wildcard DNS entries for VMs is not supported. For feedback, contact Replicated support.
CLI
replicated vm port expose VMID_OR_VMNAME --port PORT --protocol PROTOCOL
For example, to expose port 3000 with HTTP protocol:
replicated vm port expose VM_ID --port 30000 --protocol http
Vendor Portal
To update the ingress and ports settings for a VM:
-
In the Vendor Portal, go to Compatibility Matrix.
-
Create a VM.
-
Open the dot menu for the VM and click Edit VM.
-
Under Ingress & Ports, for Add DNS record, edit the fields as desired and click Add to create a DNS record.
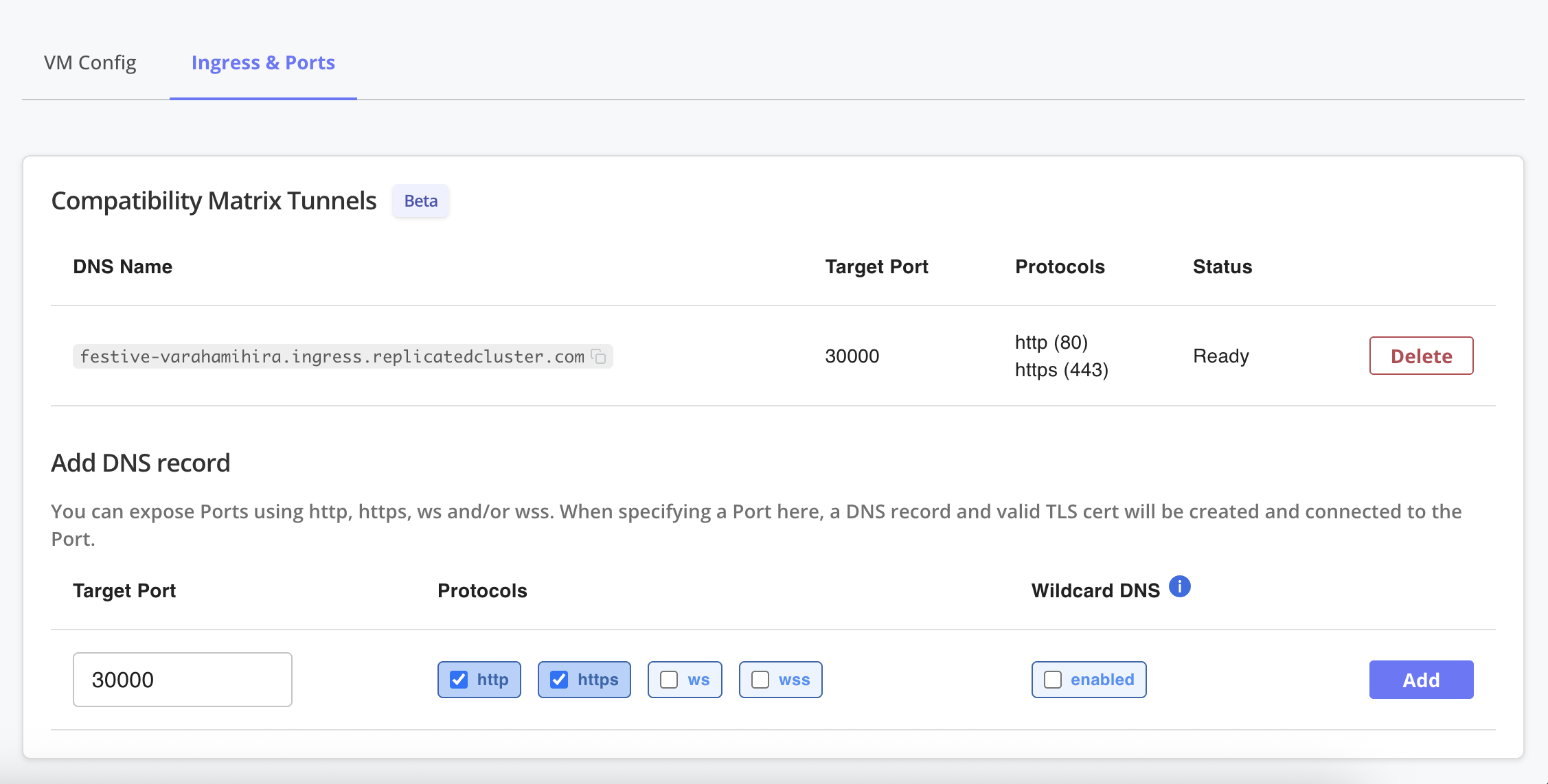 View a larger version of this image
View a larger version of this imageA DNS record and valid TLS cert are created and connected to the specified port.
Expose Ports on VM-Based Clusters
After you have a node port available on the cluster, you can expose the node port to the public internet using the Replicated CLI. There is no limit to the number of tunnels you can create for a cluster and multiple tunnels can connect to a single service.
You can expose a node port that does not yet exist in the cluster. This is useful if you have a deterministic node port, but need the DNS name as a value in your Helm chart.
The following diagram shows how the traffic is routed into the service using Compatibility Matrix tunnels:
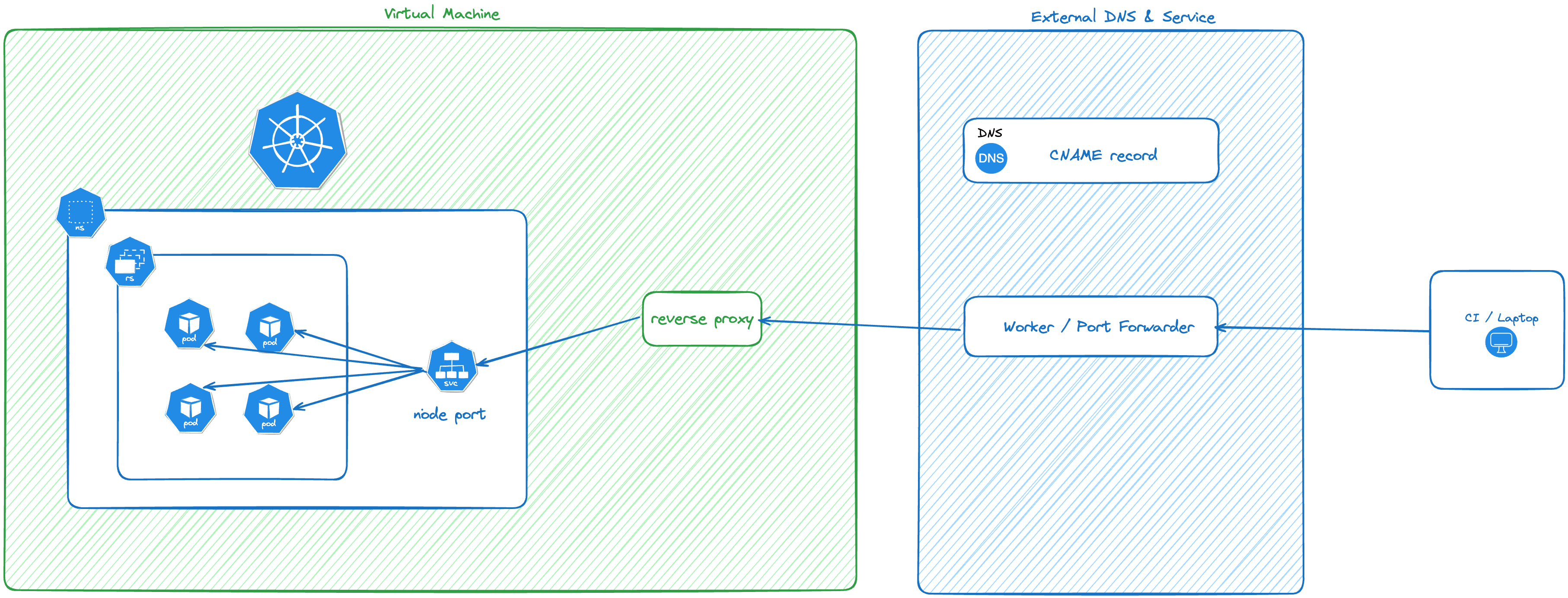
View a larger version of this image
Limitations
- A tunnel can only connect to one service. If you need fanout routing into different services, consider installing the nginx ingress controller as a
NodePortservice and exposing it. - Tunnels are not supported for cloud distributions (EKS, GKE, AKS).
Supported Protocols
A tunnel can support one or more protocols. The supported protocols are HTTP, HTTPS, WS and WSS. GRPC and other protocols are not routed into the cluster.
Expose Ports with the CLI
To expose a port on a cluster using the Replicated CLI:
replicated cluster port expose \
[cluster id] \
--port [node port] \
--protocol [protocol]
See cluster port.
Use Wildcard DNS
Optionally, you can specify the --wildcard flag to expose this port with wildcard DNS and TLS certificate.
This feature adds extra time to provision the port, so it should only be used if necessary.
For example, if you have the nginx ingress controller installed and the node port is 32456:
% replicated cluster ls
ID NAME DISTRIBUTION VERSION STATUS
1e616c55 tender_ishizaka k3s 1.29.2 running
% replicated cluster port expose \
1e616c55 \
--port 32456 \
--protocol http \
--protocol https \
--wildcard
View Exposed Ports
To view all exposed ports, use the replicated port ls subcommand with the cluster or VM ID:
replicated cluster port ls CLUSTER_ID
replicated vm port ls VMID_OR_VMNAME
Remove Ports
Exposed ports are automatically deleted when the cluster or VM terminates.
If you want to remove a port (and the associated DNS records and TLS certs) prior to termination, run the port rm subcommand with the cluster or VM ID:
replicated cluster port rm PORT_ID --id CLUSTER_ID
replicated vm port rm VMID_OR_VMNAME
You can remove just one protocol, or all. Removing all protocols also removes the DNS record and TLS cert.